Structure of Fiber Optic Cables - What is Fiber Optic Cable?
A fiber optic cable is a Silicon Dioxide (Silicon Dioxide-SiO₂) glass material through which light is directed. The most important reason why fiber optic cables are produced in this way and are preferred is that they are not affected by humid, damp places where environmental conditions are severe and where electrical field interference is intense and they always offer a stable connection.
The biggest advantage of fiber optic cable comparing with the CAT copper one is the bandwidth and long distances it provides can be shown as Data transport superiority in a lossless and full performance way. Data carrying distance in CAT copper cables is limited to a maximum of 100 meters. In order to carry data over distances of more than 100 meters, a requirement of Switch installation occurs at every 100 meters. For this reason, fiber optic cables are designed for data transmission over long distances, as they perform Data transmission with the speed of light at 300.000/km per second.
Types of Fiber Optic Cable
1- Zipcord Fiber Optic Cable
Zipcord Fiber Optic Cable type is a type of Duplex (bi-directional) cable that is used in active device connections and does not require termination. In other words, this is the type of Fiber Optic cable that System and Network experts will see in server rooms.
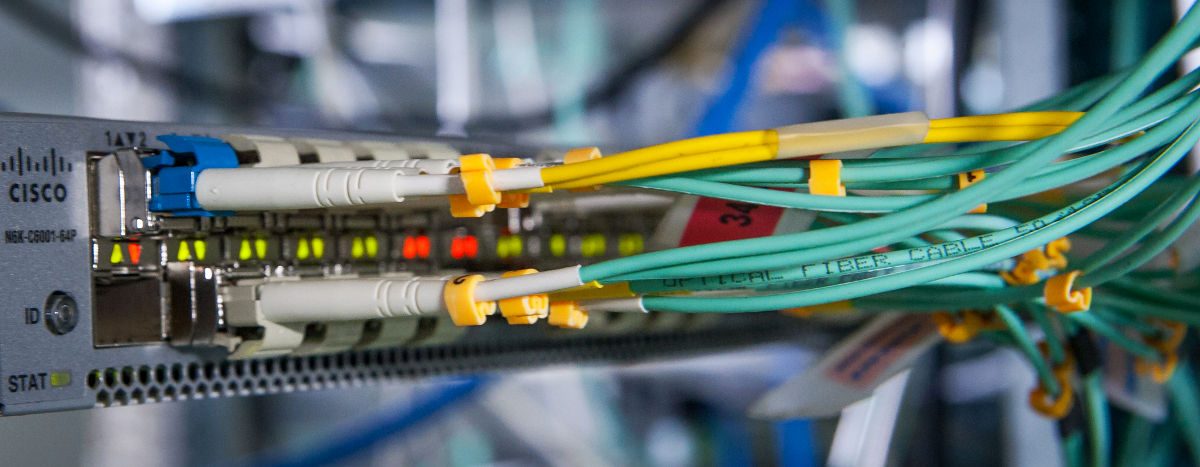

2- Multi-Core Fiber Optic Cables
There are Multi Core Fiber Optic cables that connect countries, even continents, with the Internet. These cables are laid on the sea and ocean floors or underground in cities. For this reason, if you are not working for a company that does this job, it is unlikely that you will see Multi Core Fiber Optic cables.
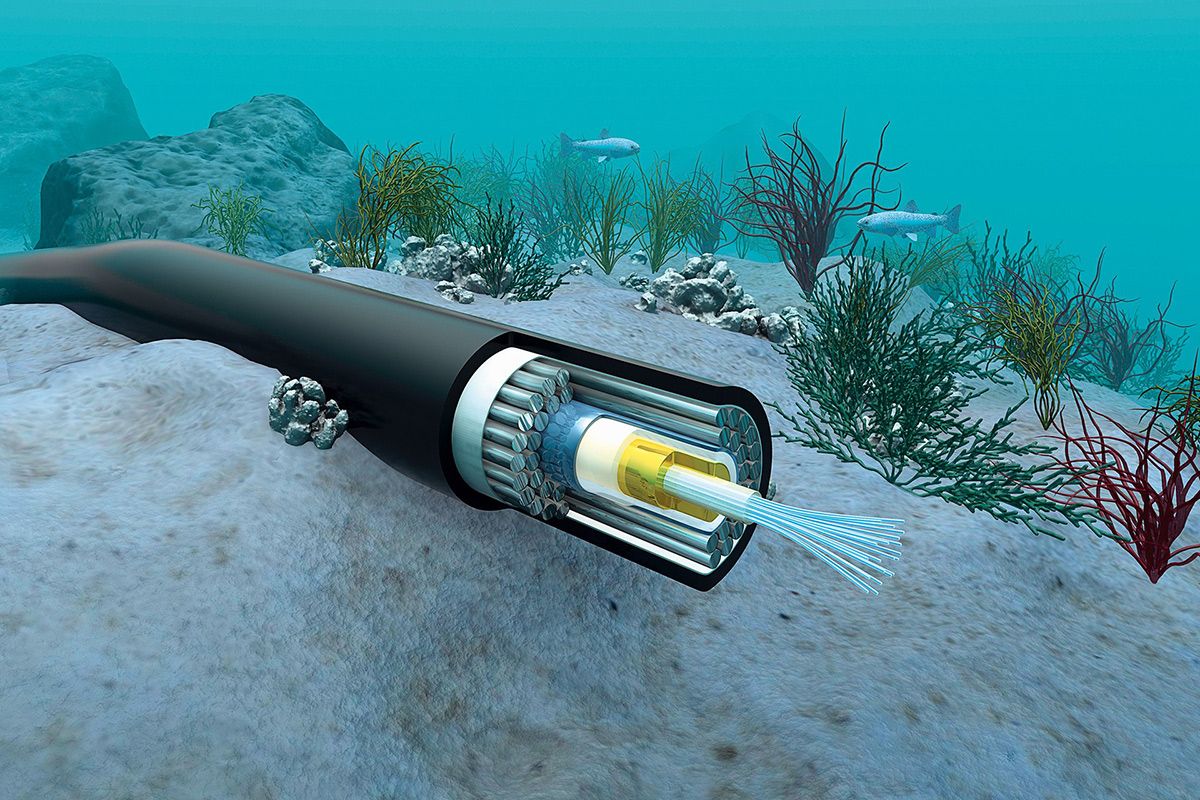

To show the structural visuals of some multi-core fiber optic cables;
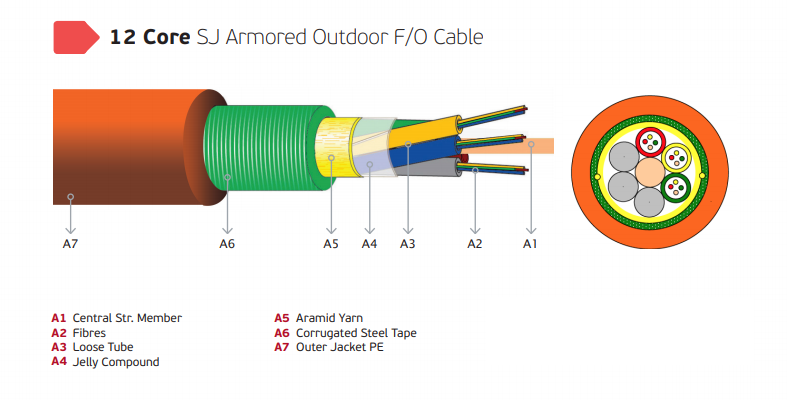
12 Core Multi Core Fiber Optic Cable
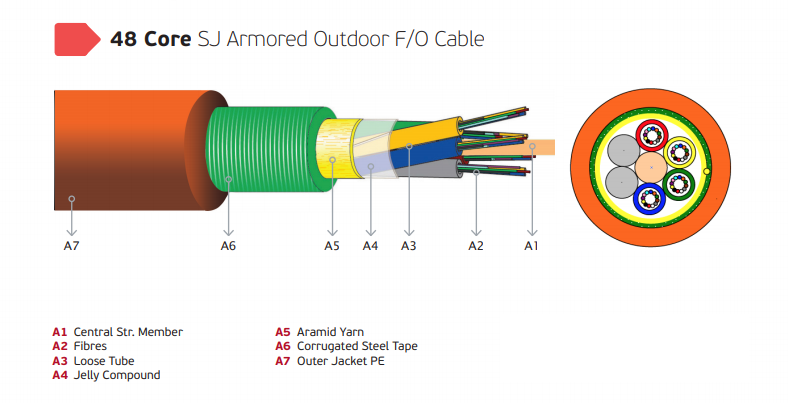
48 Core Multi Core Fiber Optic Cable
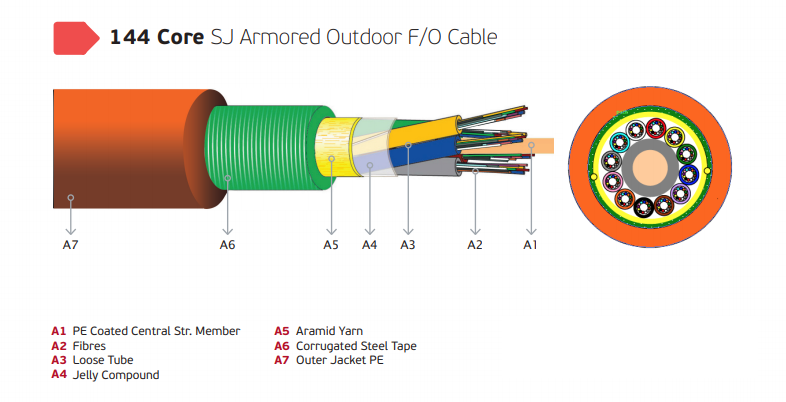
144 Core Multi Core Fiber Optic Cable
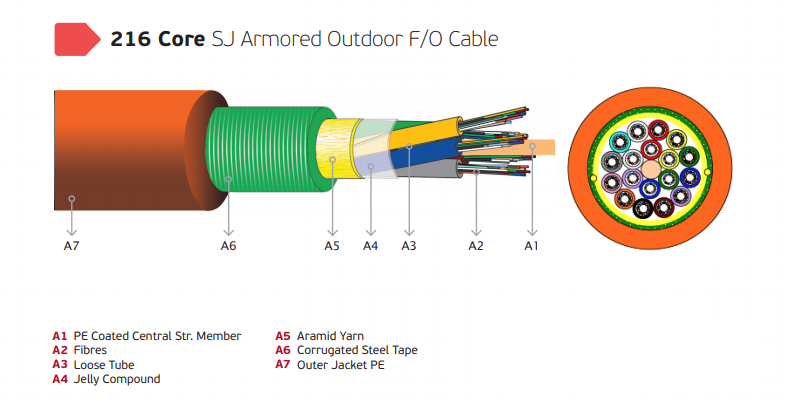
216 Core Multi Core Fiber Optic Cable
Zipcord Fiber Optic Cable
The simplest form of Fiber Optic cables is Zipcord Fiber Optic cable that you can see in your system rooms or Data Centers. Multi-Core Fiber Optic cables installed in the ocean, sea or underground are covered with much more insulation material as they need to be protected from external factors. Here, I will explain the Fiber Optic cable structure according to Zipcord Fiber Optic cable type.
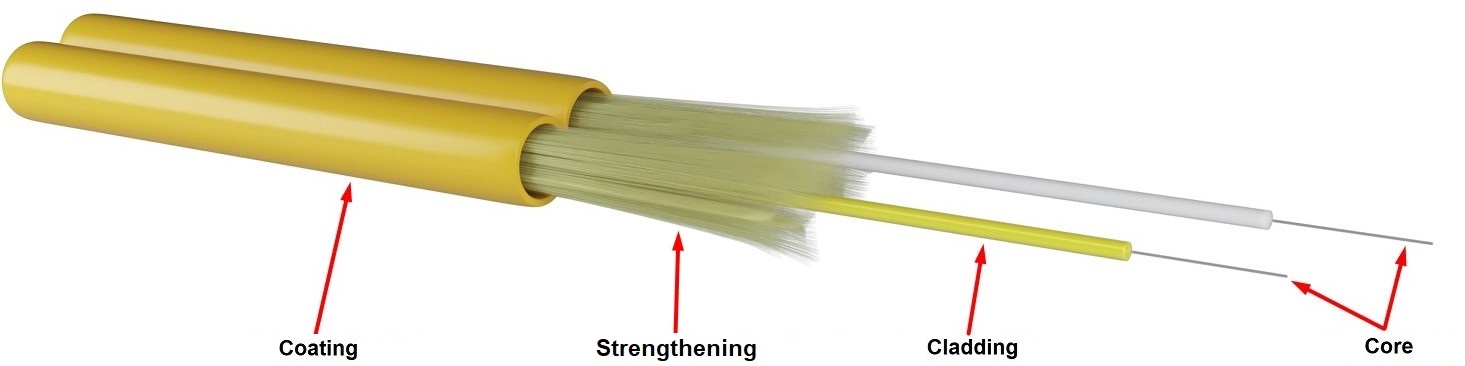
A Zipcord Fiber Optic Cable consists of three layers from the inside, out;
1- Core: It is a glass material in the structure of Silicon Dioxide - Silicon Dioxide SiO₂ to which the light is directed.
2- Cladding: It is the coating structure surrounding the core. This coating prevents the reflection of light from the core and thus data loss.
3- Strengthening: It is the load-bearing component of the fiber optic cable. This component is added to protect the cladding and especially the core in the fiber optic cable against the situations such as tensile. It is purely for security purposes.
4- Coating: The outmost coating enclosing the coating that encloses the core.
Fiber Optic Cable Types and Cladding - Core Diameter
Today, there are two types of Fiber Optic Cable: Multimode (multi mode) Fiber Optic Cable and Singlemode (single mode) Fiber Optic Cable.
1- Multimode Fiber Optic Cable
It has an outer diameter (cladding) of 125µm (micrometer) , core diameter of from 62.5µm to 50µm and a Wave Length of 850 to 1300 nanometers, and the core is much larger than Singlemode.
Multimode Fiber cables are divided into 2(two) according to their index structure;
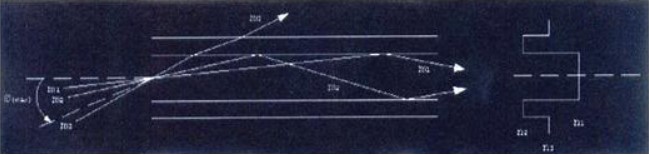
1- Step-Index Multimode Fiber Optic Cable
This type of Fiber has a larger light aperture, thus allowing more light to flow through the cable. Light rays that strike the boundary between the core and the cladding at an angle greater than the critical angle emit in a zigzag pattern in the core and are continuously reflected from the boundary.
Light rays striking the boundary between the core and the cladding at an angle smaller than the critical angle enter the cladding and disappear. It can be seen that there are many paths that light beams can follow as they emit at the fiber. As a result, all light rays do not follow the same path, so they do not travel the distance from one end of the fiber to the other in the same time period.
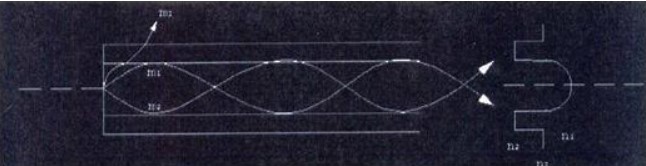
2- Graded-Index Multimode Fiber Optic Cable
The index of the core in the structure of the degree-indexed Multimode Fiber changes depending on the radius. In other words, it is in the form of concentric rings from the inside out. The refractive index of each of these rings is different and the refractive index decreases as you go from the inside to the outside. In other words, there is the largest index in the center and the smallest index in the outermost.
The light that goes directly in the center travels little; however, the index here is large. The distance taken by the lights traveling in the more outer layers is more; However, since the index is small in these layers, the speed of light varies inversely with the index profile. Hence, all lights converge at certain nodal points; however, there is a delay between pulses at the receiving end. However, the delay rate is less than the step index Multimode Fibers.
2- Singlemode Fiber Optic Cable
It has an outer (cladding) diameter of 125µm (micrometer or micron), core diameter of 9µm and Wave Length between 1300 and 1550 nanometers, and core has a narrower structure compared to multimode.
Since the core diameter has a very small diameter of 9µm, there is only one way the light can follow while it is transmitting in the cable. There is only one mode or direction of light in the fiber that travels at a specific wavelength. Thus, all light rays follow approximately the same path in the cable, and the distance from one end of the cable to the other in approximately the same time. This is one of the most important advantages of Singlemode cables. Also, since there is only one light mode in this cable type, there is no modal radiation. This provides less propagation loss and more information carrying capacity.

NOTE: Singlemode Fiber optic cables are preferred for longer distances than Multimode Fiber optic cables.
What I have tried to explain so far is that Cladding - Core diameters are of great importance in terms of the wave length of the light transmitted through the core and the data capacity and quality it carries along its path during transmission. These diameters also directly affect the distance of the Data to be carried over the cable.
Multimode Fiber Optic Cable Structures and Distances
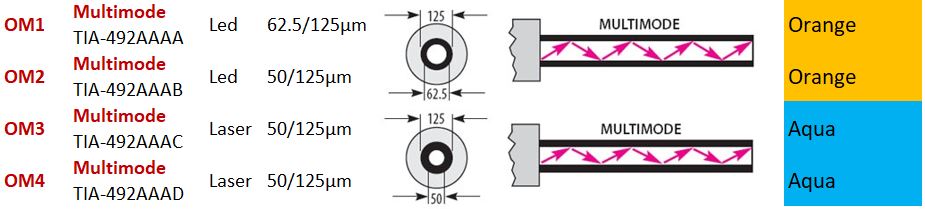
We can classify Multimode Fiber optic cable according to their structures and data transmission rates as follows:
OM1-Multimode (TIA492AAAA):
ORANGE colored with LED light. Outer diameter is 125µm and core diameter is 62.5µm.
|
Platform |
Speed |
Distance |
Standard |
|
Fast Ethernet |
100 Mbps |
2 KM. |
100BASE-FX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
275 MT. |
1000BASE-SX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
550 MT. |
1000BASE-LX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
33 MT. |
10GBASE-E |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
Not applied. |
40GBASE |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
100 Gbps |
Not applied. |
1000BASE-SX |
OM2-Multimode (TIA492AAAB):
ORANGE colored with LED light. Outer diameter is 125µm and core diameter is 50µm.
|
Platform |
Speed |
Distance |
Standard |
|
Fast Ethernet |
100 Mbps |
2 KM. |
100BASE-FX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
550 MT. |
1000BASE-SX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
550 MT. |
1000BASE-LX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
82 MT. |
10GBASE-E |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
Not applied. |
40GBASE |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
100 Gbps |
Not applied. |
1000BASE-SX |

OM3-Multimode (TIA492AAAC):
AQUA colored with LAZER light. Outer diameter is 125µm and core diameter is 50µm.
|
Platform |
Speed |
Distance |
Standard |
|
Fast Ethernet |
100 Mbps |
2 KM. |
100BASE-FX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
550 MT. |
1000BASE-SX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
550 MT. |
1000BASE-LX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
300 MT. |
10GBASE-E |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
100 MT. |
40GBASE |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
100 Gbps |
100 MT. |
1000BASE-SX |
OM4-Multimode (TIA492AAAD):
AQUA colored with LAZER light. Outer diameter is 125µm and core diameter is 50µm.
|
Platform |
Speed |
Distance |
Standard |
|
Fast Ethernet |
100 Mbps |
2 KM. |
100BASE-FX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
550 MT. |
1000BASE-SX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
550 MT. |
1000BASE-LX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
400 MT. |
10GBASE-E |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
150 MT. |
40GBASE |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
100 Gbps |
150 MT. |
1000BASE-SX |

Structures and Distances of Singlemode Fiber Optic Cable
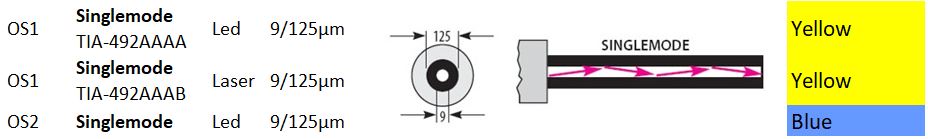
We can classify Singlemode Fiber optic cable according to their structures and data transmission rates as follows:
OS1-Singlemode (TIA492AAAA):
YELLOW colored with LED light. Outer diameter is 125µm and core diameter is 9µm.
|
Platform |
Speed |
Distance |
Standard |
|
Fast Ethernet |
100 Mbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 2 KM. |
100BASE-FX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 5 KM. |
1000BASE-SX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 5 KM. |
1000BASE-LX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 40 KM. |
1000BASE-EX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 70 KM. |
1000BASE-ZX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 70 KM. |
1000BASE-LH |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 10 KM. |
10GBASE-LR |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 10 KM. |
10GBASE-SR |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 40 KM. |
10GBASE-ER |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 80 KM. |
10GBASE-ZR |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 10 KM. |
40GBASE-LR4 |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 40 KM. |
40GBASE-ER4 |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 10 KM. |
100GBASE-LR4 |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 40 KM. |
100GBASE-ER4 |
OS1-Singlemode (TIA492AAAB):
YELLOW colored with LAZER light. Outer diameter is 125µm and core diameter is 9µm.
|
Platform |
Speed |
Distance |
Standard |
|
Fast Ethernet |
100 Mbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 2 KM. |
100BASE-FX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 5 KM. |
1000BASE-SX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 5 KM. |
1000BASE-LX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 40 KM. |
1000BASE-EX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 70 KM. |
1000BASE-ZX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 70 KM. |
1000BASE-LH |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 10 KM. |
10GBASE-LR |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 10 KM. |
10GBASE-SR |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 40 KM. |
10GBASE-ER |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 80 KM. |
10GBASE-ZR |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 10 KM. |
40GBASE-LR4 |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 40 KM. |
40GBASE-ER4 |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 10 KM. |
100GBASE-LR4 |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 40 KM. |
100GBASE-ER4 |

OS2-Singlemode:
BLUE colored with LAZER light. Outer diameter is 125µm and core diameter is 50µm.
|
Platform |
Speed |
Distance |
Standard |
|
Fast Ethernet |
100 Mbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 2 KM. |
100BASE-FX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 5 KM. |
1000BASE-SX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 5 KM. |
1000BASE-LX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 40 KM. |
1000BASE-EX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 70 KM. |
1000BASE-ZX |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 70 KM. |
1000BASE-LH |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 10 KM. |
10GBASE-LR |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 10 KM. |
10GBASE-SR |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 40 KM. |
10GBASE-ER |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
10 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 80 KM. |
10GBASE-ZR |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 10 KM. |
40GBASE-LR4 |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 40 KM. |
40GBASE-ER4 |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
in 1310(nm) nanometer 10 KM. |
100GBASE-LR4 |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
40 Gbps |
in 1550(nm) nanometer 40 KM. |
100GBASE-ER4 |

I hope it benefits...
Tags: What is fiber optic cable?, Fiber optic cable speeds,bandwidth, OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, Multimode Fiber optic cable types, OS1, OS2, Singlemode Fiber optic cable types, gigbitethernet, fastethernet
You may submit your any kind of opinion and suggestion and ask anything you wonder by using the below comment form.